Brief Information about AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
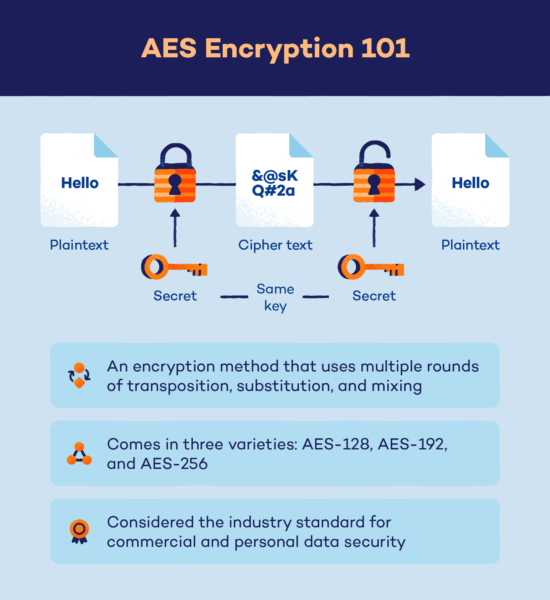
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a symmetric encryption algorithm widely used for securing sensitive data. It was established as the standard by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001, replacing the aging Data Encryption Standard (DES). AES operates on fixed-size blocks of data, encrypting and decrypting information in a way that is both secure and efficient.
Detailed Information about AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES is a block cipher, meaning it encrypts data in fixed-size blocks. It supports key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits, with the larger key sizes providing stronger encryption. The algorithm consists of multiple rounds of substitution, permutation, and mixing operations, ensuring a high level of security. AES encrypts data using a series of transformations, including substitution of bytes, shifting of rows, mixing of columns, and adding round keys.
Detailed Analysis of the Key Features of AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
Key features of AES include:
- Symmetric Encryption: AES uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, making it faster and simpler compared to asymmetric encryption algorithms.
- Variable Key Lengths: AES supports key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits, allowing users to choose the level of security they require.
- High Security: AES has withstood extensive cryptanalysis and is considered secure against brute-force attacks when implemented correctly.
- Efficiency: AES is computationally efficient and can be implemented in hardware and software, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Standardization: AES is a widely adopted standard, used in various industries and applications worldwide.
Types of AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
| Key Size (bits) | Rounds |
|---|---|
| 128 | 10 |
| 192 | 12 |
| 256 | 14 |
Ways to Use AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES can be used in various applications, including:
- Data Encryption: Secure sensitive information such as financial transactions, personal data, and confidential communications.
- File Encryption: Protect files and documents stored on computers or transmitted over networks.
- Disk Encryption: Encrypt entire hard drives or partitions to prevent unauthorized access to data.
- Communication Security: Secure communication channels, such as VPNs, SSL/TLS, and SSH, to protect data during transmission.
- Database Encryption: Encrypt databases to safeguard stored data from unauthorized access.
Problems and Solutions with the Use of AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
Challenges with AES implementation may include:
- Key Management: Ensuring secure key generation, storage, and distribution to authorized parties.
- Side-Channel Attacks: Protecting against attacks that exploit unintended information leakage, such as timing or power consumption.
- Cryptographic Vulnerabilities: Addressing potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities discovered through cryptanalysis.
- Performance Overhead: Balancing security requirements with performance considerations, especially in resource-constrained environments.
Solutions to these challenges involve implementing best practices for key management, using secure cryptographic libraries, regularly updating encryption protocols, and conducting thorough security audits.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons with Similar Terms
| Characteristic | AES | DES (Data Encryption Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Key Size | 128, 192, 256 bits | 56 bits |
| Block Size | 128 bits | 64 bits |
| Rounds | 10, 12, 14 | 16 |
| Security | High | Low (considered insecure) |
| Standardization | Widely adopted standard | Deprecated |
| Performance | Efficient | Relatively slow |
Perspectives and Future Technologies Related to AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
As technology evolves, AES continues to be a foundational component of secure communication and data protection. Future advancements may include:
- Quantum-Safe Cryptography: Developing encryption algorithms resilient to attacks from quantum computers.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Researching and standardizing new cryptographic primitives resistant to quantum attacks.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Advancing techniques for performing computations on encrypted data without decryption, enabling secure data processing in cloud environments.
- Hardware Acceleration: Utilizing specialized hardware accelerators to enhance the performance of AES encryption and decryption operations.
VPN and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES is commonly used in VPN (Virtual Private Network) protocols to secure data transmitted over the internet. By encrypting network traffic with AES, VPNs ensure privacy and confidentiality, protecting users from eavesdropping and surveillance. AES encryption combined with VPN technologies such as IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) or OpenVPN provides a secure and private communication channel for users, whether accessing the internet from home, office, or public Wi-Fi networks.
Links to Resources for More Information about AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
For further reading on AES and related topics, please refer to the following resources:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – AES Information: https://csrc.nist.gov/Projects/Advanced-Encryption-Standard-AES
- Crypto101: Introduction to Modern Cryptography: https://crypto101.io/
- Schneier on Security: https://www.schneier.com/
These resources offer in-depth explanations, technical specifications, and insights into the use of AES in modern cryptography and information security.