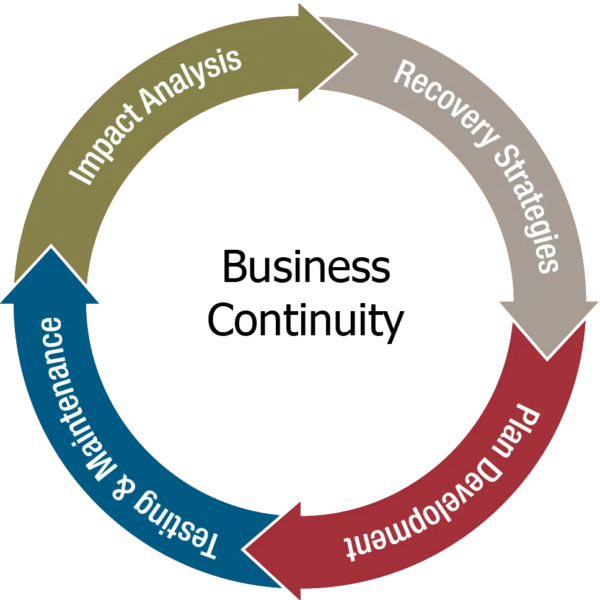
Brief Information about Business Continuity
Business Continuity refers to the strategic and procedural approach that organizations undertake to ensure the continued operation of critical business functions during and after a disaster or unforeseen event. It encompasses a comprehensive plan that addresses various aspects of an organization’s operations, including technology, personnel, facilities, and communication.
Detailed Information about Business Continuity
Business Continuity planning involves identifying potential threats and risks to business operations, assessing their potential impact, and developing strategies to mitigate these risks. The goal is to minimize downtime, maintain essential services, and safeguard the organization’s reputation and financial stability.
Detailed Analysis of Key Features of Business Continuity
Key features of Business Continuity include risk assessment, business impact analysis, development of continuity plans and procedures, crisis communication strategies, and regular testing and updating of the plan. These features ensure that organizations can respond effectively to disruptions and resume operations as quickly as possible.
Types of Business Continuity
Business Continuity plans can be categorized into various types based on their scope and focus:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| IT Disaster Recovery | Focuses on restoring critical IT systems and data in the event of a technology-related disaster. |
| Crisis Management | Involves coordination of response efforts during a crisis to minimize its impact on operations. |
| Workplace Recovery | Addresses the need for alternative workspaces and infrastructure to support business operations. |
| Supply Chain Continuity | Ensures the continuity of critical supply chain functions to prevent disruptions in production. |
Ways to Use Business Continuity
Organizations can leverage Business Continuity in various ways, including:
- Ensuring uninterrupted service delivery to customers.
- Protecting sensitive data and information.
- Safeguarding the organization’s reputation and brand.
- Complying with regulatory requirements.
- Minimizing financial losses associated with downtime.
Problems and Solutions with Business Continuity
Challenges that organizations may encounter with Business Continuity include:
- Lack of senior management buy-in and support.
- Insufficient resources and budget constraints.
- Complex organizational structures and dependencies.
- Difficulty in accurately assessing and prioritizing risks.
These challenges can be addressed through:
- Executive-level commitment and involvement in the planning process.
- Adequate allocation of resources and funding for Business Continuity initiatives.
- Streamlining processes and ensuring clear communication channels.
- Regular training and testing exercises to identify and address gaps in the plan.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons
Business Continuity is often compared with other related terms such as Disaster Recovery and Risk Management. Here are some main characteristics and comparisons:
| Aspect | Business Continuity | Disaster Recovery | Risk Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Comprehensive | IT-focused | Broadly focused on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. |
| Objective | Maintain operations | Restore IT systems | Manage risks to achieve business objectives. |
| Focus | Prevention and preparedness | Response and recovery | Identification and mitigation of risks. |
Perspectives and Future Technologies
As technology continues to evolve, the future of Business Continuity will likely see advancements in:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for predictive analysis and risk assessment.
- Cloud-based solutions for enhanced scalability and accessibility.
- Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time monitoring and response.
- Blockchain for secure and immutable data storage and verification.
VPN and Business Continuity
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) play a crucial role in Business Continuity by providing secure remote access to corporate networks and resources. During a crisis or disaster, employees can use VPNs to connect to their organization’s network from any location, ensuring continuity of operations even when physical access to the workplace is restricted. VPNs also encrypt data transmission, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or interception.
Links to Resources
For more information about Business Continuity, refer to the following resources:
- Business Continuity Institute (BCI): https://www.thebci.org/
- Disaster Recovery Journal (DRJ): https://www.drj.com/
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): https://www.iso.org/iso-22301-business-continuity.html
These organizations provide valuable insights, best practices, and standards for effective Business Continuity planning and implementation.