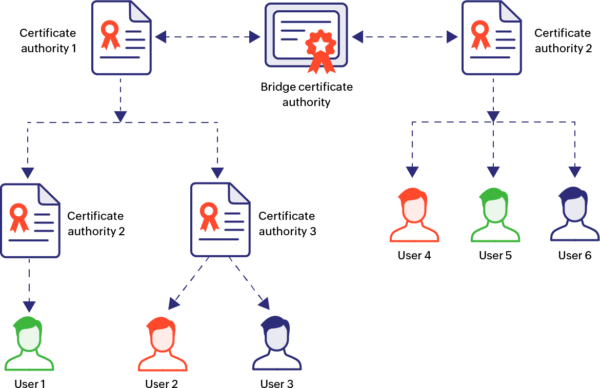
Certificate Authority (CA) plays a pivotal role in securing online communications by issuing digital certificates that authenticate the identities of entities in cyberspace. These entities can range from individuals and organizations to websites and devices. The CA acts as a trusted third party responsible for verifying the authenticity of these entities, thereby establishing trust in the digital realm.
Overview
A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity responsible for issuing digital certificates that verify the authenticity of a party’s identity on the internet. These certificates serve as electronic credentials, allowing users to securely communicate and transact online.
Expanding the Topic
Certificate Authorities utilize cryptographic algorithms to create digital signatures that bind a public key to an entity’s identity. When a user encounters a digital certificate, their browser or application can verify its authenticity by checking its signature against the CA’s public key, which is pre-installed in the software’s trust store.
Key Features
The key features of Certificate Authorities include:
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of entities requesting digital certificates.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data transmitted over the internet to ensure confidentiality.
- Integrity: Ensuring the integrity of data by detecting any unauthorized modifications.
- Non-repudiation: Preventing parties from denying their involvement in a transaction.
Types of Certificate Authorities
There are several types of Certificate Authorities, including:
- Public CAs: Trusted third-party entities that issue digital certificates to the public. Examples include Let’s Encrypt and DigiCert.
- Private CAs: Internal CAs used by organizations to issue certificates for their internal network infrastructure.
- Root CAs: The highest level of authority in the certificate hierarchy, responsible for issuing and managing subordinate CAs.
- Intermediate CAs: CAs that are subordinate to root CAs and issue certificates on their behalf.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Public CAs | Trusted third-party entities issuing certificates to public |
| Private CAs | Used by organizations for internal network infrastructure |
| Root CAs | Highest level of authority in certificate hierarchy |
| Intermediate CAs | Subordinate to root CAs, issuing certificates on their behalf |
Uses of Certificate Authority
Certificate Authorities are utilized in various ways, including:
- Secure website communication via HTTPS.
- Authentication in virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Email encryption and digital signatures.
- Code signing to verify the authenticity of software.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite their importance, Certificate Authorities face challenges such as:
- Certificate misissuance leading to security vulnerabilities.
- Trust issues due to compromised or rogue CAs.
- Management of certificate revocation lists (CRLs) and certificate transparency logs.
These challenges can be mitigated through:
- Strict validation processes for certificate issuance.
- Regular audits and compliance checks for CAs.
- Implementation of certificate transparency mechanisms.
Characteristics and Comparisons
| Characteristic | Certificate Authority | Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Issuing digital certificates | Framework for managing public/private keys |
| Scope | Can be public or private | Encompasses multiple entities and protocols |
| Trust Model | Relies on trust in CA’s integrity | Establishes trust through hierarchical structure |
| Security Mechanisms | Public key cryptography, digital signatures | Encryption, authentication, integrity |
| Examples | Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert | X.509, SSL/TLS protocols |
Future Perspectives and Technologies
Future developments in Certificate Authority technology may include:
- Increased use of blockchain for decentralized certificate issuance.
- Integration with emerging technologies such as quantum-resistant cryptography.
- Automation of certificate lifecycle management through machine learning and AI algorithms.
VPN and Certificate Authority
VPN services often rely on digital certificates issued by Certificate Authorities to authenticate users and secure communications. By integrating with CAs, VPNs can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data transmitted over the network.
Resources
For more information about Certificate Authority, refer to the following resources:
- “RFC 5280 – Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Profile”
- “Certificate Authority Security Council (CASC) – https://casecurity.org/“
- “Certificate Transparency – https://www.certificate-transparency.org/“
This comprehensive article elucidates the intricacies of Certificate Authority, its applications, challenges, and future prospects, serving as a valuable resource for understanding the critical role it plays in securing online communications.