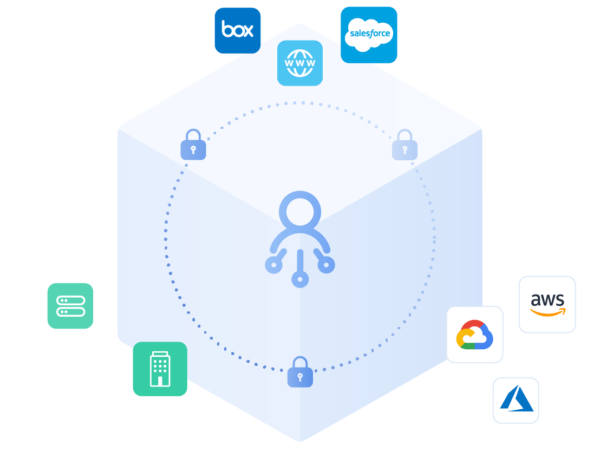
Cloud Virtual Private Networks (Cloud VPNs) are evolving as a pivotal part of modern network architecture, offering enhanced security, scalability, and flexibility. This technology enables businesses and individuals to securely access cloud services and corporate networks over the internet, ensuring data privacy and integrity through encrypted connections.
Understanding Cloud VPN
Cloud VPN, also known as a VPN-as-a-Service (VPNaas), is a cloud-based service that creates a secured, encrypted connection over the internet from a device to a network, ensuring safe data transmission. This technology leverages cloud resources to provide VPN services to users, offering a scalable, flexible solution for secure remote access.
Detailed Exploration of Cloud VPN
Expanding on the concept, Cloud VPN services are designed to support the dynamic and distributed nature of today’s digital work environments. Unlike traditional VPNs that require dedicated hardware and significant management effort, Cloud VPNs utilize the cloud’s infrastructure, reducing the complexity and cost of VPN deployment and maintenance.
Key Features of Cloud VPN
- Scalability: Easily adjusts to the changing needs of businesses.
- Cost-effectiveness: Eliminates the need for physical hardware and maintenance.
- Security: Provides advanced encryption and authentication methods.
- Flexibility: Supports various devices and operating systems.
- Ease of Management: Centralized management consoles for simplified administration.
Types of Cloud VPN
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Site-to-Site | Connects entire networks to each other, suitable for connecting branch offices to a central corporate network. |
| Remote Access | Allows individual users to connect to a network from any location, ideal for remote workers. |
Applications of Cloud VPN
- Secure Remote Access: Enables employees to safely access corporate resources from anywhere.
- Business Continuity: Ensures business operations can continue by providing secure access to necessary applications and data.
- Cloud Services Integration: Facilitates secure connectivity between on-premises networks and cloud environments.
Challenges with Cloud VPN and Solutions
Challenges:
- Security Concerns: Potential vulnerabilities could expose data to risks.
- Performance Issues: Internet-based connections may suffer from latency.
Solutions:
- Implementing robust encryption and authentication mechanisms.
- Choosing cloud VPN providers with a strong network infrastructure to minimize latency.
Comparative Analysis with Similar Technologies
| Feature | Cloud VPN | Traditional VPN | Direct Connect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-based | Physical or software-based | Physical connection to a data center |
| Scalability | High | Limited by hardware | Fixed capacity |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go | Upfront hardware/software cost | High initial setup and monthly fees |
| Flexibility | High | Medium | Low |
Future Trends in Cloud VPN Technology
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: For predictive security and performance optimization.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Evolving security models that do not inherently trust any entity inside or outside the network.
- Enhanced Cloud Interoperability: Better integration across different cloud service providers.
Utilizing VPN with Cloud VPN
Traditional VPNs can be integrated with Cloud VPN solutions to provide a layered security approach, combining the robustness of physical VPN appliances with the flexibility and scalability of cloud-based services. This hybrid approach can optimize security, performance, and cost-effectiveness for businesses.
Further Reading and Resources
- Official Cloud VPN Provider Documentation: For specifics on features, configurations, and best practices.
- Industry Whitepapers and Case Studies: Offering insights into deployment scenarios and benefits.
- Security and Technology Blogs: For the latest trends, challenges, and advancements in Cloud VPN technology.
This comprehensive guide to Cloud VPN offers a deep dive into its workings, benefits, and challenges, providing a solid foundation for understanding how this technology can be leveraged to enhance network security and performance in a cloud-centric world.