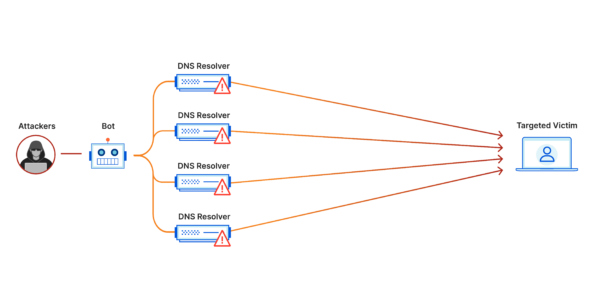
Brief Information:
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service, or network by overwhelming it with a flood of internet traffic. This onslaught of traffic comes from a multitude of sources, making it difficult to mitigate and often resulting in a complete or partial denial of service to legitimate users.
Detailed Information:
DDoS attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols or applications to flood the targeted system with an overwhelming amount of traffic. The goal is to exhaust the target’s resources such as bandwidth, CPU, or memory, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. These attacks can be launched from a single source, but more commonly, they are orchestrated from multiple distributed sources, hence the term “distributed” denial of service.
Key Features Analysis:
Key features of DDoS attacks include:
- Volume: Massive amounts of traffic are generated to overwhelm the target.
- Distribution: Attacks originate from multiple sources, making it harder to mitigate.
- Variety: DDoS attacks come in various forms, including volumetric, protocol, and application layer attacks.
- Botnets: Attackers often leverage botnets, networks of compromised devices, to orchestrate DDoS attacks.
Types of DDoS Attacks:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Volumetric Attacks | Flood the target with a high volume of traffic, consuming all available bandwidth. |
| Protocol Attacks | Exploit weaknesses in network protocols (e.g., TCP/IP) to exhaust server resources. |
| Application Layer | Target specific applications or services (e.g., HTTP, DNS) to overwhelm the server with requests. |
Ways to Use DDoS Attacks:
- Cyber Warfare: DDoS attacks are often used as a weapon in cyber warfare to disrupt critical infrastructure.
- Extortion: Attackers may demand ransom to cease the attack and restore services.
- Competitive Advantage: In some cases, DDoS attacks are used by competitors to gain an advantage by disrupting a rival’s services.
- Hacktivism: Activists may launch DDoS attacks to protest against organizations or governments.
Problems and Solutions:
Challenges associated with DDoS attacks include:
- Service Disruption: DDoS attacks can result in significant downtime and financial losses for businesses.
- Detection and Mitigation: Identifying and mitigating DDoS attacks in real-time can be challenging.
- Botnet Resilience: Botnets used to launch DDoS attacks are often resilient and difficult to dismantle.
Solutions to mitigate DDoS attacks include:
- Network Filtering: Implementing traffic filtering mechanisms to block malicious traffic.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Using CDNs to distribute traffic and absorb DDoS attacks.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploying IDS to detect and respond to DDoS attacks in real-time.
Characteristics and Comparisons:
| Characteristic | DDoS Attack | Similar Terms |
|---|---|---|
| Intent | Malicious | Cybersecurity Threat |
| Method | Flood of traffic from multiple sources | Cyber Attacks |
| Impact | Service disruption | Network Security Breaches |
| Motivation | Financial gain, sabotage, hacktivism | Cybercrime |
Future Perspectives and Technologies:
- AI and Machine Learning: Utilizing AI-driven solutions to enhance DDoS detection and mitigation capabilities.
- Blockchain: Exploring blockchain-based solutions for more secure and resilient networks.
- Quantum Computing: Potential future advancements in quantum computing may pose both opportunities and challenges in combating DDoS attacks.
VPN and DDoS Attacks:
VPNs can play a crucial role in mitigating the risk of DDoS attacks by:
- Anonymizing Traffic: Concealing the user’s real IP address, making it harder for attackers to target them directly.
- Encryption: Encrypting data transmitted over the network, reducing the likelihood of interception or manipulation by attackers.
- Access Control: Restricting access to VPN services can help prevent unauthorized users from launching DDoS attacks through the VPN infrastructure.
Resources:
For further information on DDoS attacks, you can refer to the following resources: