Identity Management (IDM) refers to a broad administrative area that deals with identifying individuals within a system (such as a country, a network, or an organization) and controlling their access to resources within that system by associating user rights and restrictions with the established identity.
Understanding Identity Management
Identity Management encompasses the processes and technologies involved in recognizing, authenticating, and authorizing individuals who utilize computer systems, networks, and applications. It involves a comprehensive framework of policies and technologies aimed at ensuring that users are who they claim to be and that they have appropriate access to technology resources. IDM systems are used to increase security, improve productivity by streamlining and automating the user management process, and enhance compliance with legal and regulatory policies.
Detailed Analysis of Key Features of Identity Management
Key features of Identity Management include:
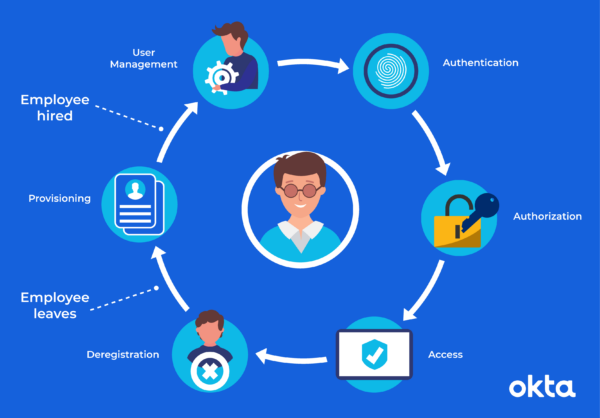
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of a user by examining their credentials.
- Authorization: Granting or denying rights to a user based on their authentication.
- User Management: Creating, managing, and removing users from an identity management system.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigning system access to users based on their role in an organization.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Allowing users to log in once and gain access to multiple systems without being prompted to log in again.
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Requiring more than one form of verification from independent categories of credentials to verify the user’s identity for a login or other transaction.
Types of Identity Management
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud-Based IDM | Services hosted in the cloud, offering scalability and flexibility. |
| On-Premises IDM | Solutions that are deployed on an organization’s own servers, offering more control over data. |
| Hybrid IDM | A combination of cloud-based and on-premises solutions. |
| Federated Identity | A system where users can use the same identification data to obtain access to the networks of multiple enterprises. |
Ways to Use Identity Management
- Enhancing Security: Protecting data from unauthorized access.
- Improving User Experience: Simplifying the login process for users with SSO.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring systems adhere to laws and regulations regarding data access and privacy.
- Efficient User Management: Automating the process of adding, removing, and managing user access.
Challenges and Solutions in Identity Management
Challenges in Identity Management include:
- Security Risks: Potential for identity theft and unauthorized access.
- Complexity: Managing identities across various platforms can be complicated.
- Compliance: Keeping up with changing regulations can be difficult.
Solutions include:
- Implementing Strong Authentication Methods: Use of MFA and biometrics.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring: To identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Education and Training: Ensuring that users are aware of security best practices.
Comparisons and Characteristics
| Feature | Identity Management | Access Management | Directory Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | User identities | User access | User information |
| Functionality | Authentication and authorization | Authorization | Information storage and retrieval |
| Implementation Complexity | High | Medium | Low |
Future Perspectives and Technologies
Emerging trends in Identity Management include:
- Blockchain for Identity Management: Offering a decentralized approach to identity verification and authentication.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: For detecting and responding to security threats in real time.
- Biometric Authentication: Increasing use of fingerprints, facial recognition, and other biometric data for secure and convenient user verification.
VPN and Its Association with Identity Management
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) can enhance Identity Management by:
- Securing Data Transmission: Encrypting data in transit to protect it from interception.
- Remote Access Security: Providing secure access to network resources for remote users.
- Anonymity and Privacy: Masking user identities and locations to protect privacy and reduce the risk of identity theft.
Resources for Further Information
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Offers comprehensive guides on identity and access management standards.
- Identity Defined Security Alliance (IDSA): Provides resources and best practices for identity security.
- Gartner Research: Offers analysis and reports on IDM technologies and market trends.
This comprehensive guide offers a deep dive into the complex world of Identity Management, highlighting its importance, functionality, and future direction. By understanding and implementing robust IDM strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, improve user experiences, and meet compliance requirements, all while preparing for the future of digital identity.