Brief Information
IPsec, short for Internet Protocol Security, is a suite of protocols used to secure internet communications at the IP layer. It provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality for data transmitted over IP networks. Originally developed for IPv6, IPsec has been widely adopted and integrated into both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
Detailed Information
IPsec functions at the network layer of the OSI model, offering security services for IP packets. It ensures that data is protected during transmission between devices by encrypting and authenticating IP packets. This encryption and authentication process occurs at the network layer, making it transparent to applications and higher-layer protocols.
Key Features of IPsec
IPsec offers several key features essential for securing network communications:
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of communicating parties to prevent unauthorized access.
- Confidentiality: Encrypts data to ensure that it remains private and cannot be intercepted by unauthorized entities.
- Integrity: Detects any unauthorized modifications to data during transit, ensuring data integrity.
- Key Management: Facilitates the secure exchange and management of cryptographic keys used for encryption and authentication.
- Anti-replay Protection: Prevents attackers from intercepting and replaying captured packets to gain unauthorized access.
Types of IPsec
There are two main modes of IPsec deployment:
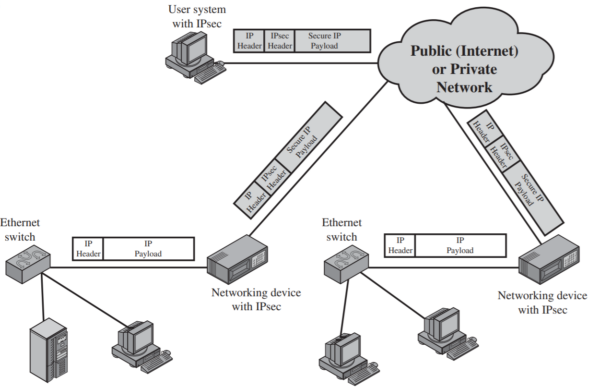
- Transport Mode: Secures communication between two endpoints, encrypting only the payload of the IP packet while leaving the header intact.
- Tunnel Mode: Encrypts both the IP header and payload of the entire packet, typically used to create virtual private networks (VPNs) between networks or remote users.
Ways to Use IPsec
IPsec is utilized in various scenarios to enhance network security:
- Secure Remote Access: Allows remote users to securely connect to corporate networks over the internet using VPNs.
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Establishes secure communication channels between geographically dispersed networks, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
- Voice and Video Conferencing: Ensures the privacy and integrity of real-time communication sessions over IP networks.
- IoT Security: Protects data transmitted between Internet of Things (IoT) devices and backend servers, safeguarding sensitive information.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its advantages, IPsec implementation may encounter challenges such as:
- Complex Configuration: Setting up and managing IPsec can be intricate, requiring expertise and careful planning.
- Performance Overhead: Encryption and decryption processes may introduce latency, impacting network performance.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring compatibility between different implementations and devices can be challenging.
To address these challenges, organizations can:
- Streamline Configuration: Utilize automated tools and templates to simplify IPsec deployment.
- Optimize Performance: Employ hardware acceleration and optimized algorithms to mitigate performance overhead.
- Standardize Implementations: Adhere to established IPsec standards and interoperability guidelines to ensure seamless integration across devices and platforms.
Characteristics and Comparisons
| Characteristic | IPsec | SSL/TLS |
|---|---|---|
| Layer of Operation | Network (Layer 3) | Transport (Layer 4) |
| Use Case | Site-to-Site VPNs, Remote Access VPNs | Web Browsing, Email Encryption |
| Encryption | IP Packet Level | Application Data Level |
| Overhead | Higher | Lower |
| Complexity | Higher | Lower |
Future Perspectives
The future of IPsec is closely tied to advancements in network security and emerging technologies such as:
- Quantum Cryptography: Developing quantum-resistant encryption algorithms to withstand future cryptographic attacks.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Integrating IPsec into SDN architectures for dynamic and scalable network security.
- Zero Trust Security: Implementing IPsec as part of a comprehensive zero trust security model to protect against insider threats and unauthorized access.
VPN and IPsec
IPsec is commonly used in conjunction with VPN technologies to create secure and private communication channels over public networks. VPNs leverage IPsec to encrypt and authenticate data transmitted between users and corporate networks, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. By combining VPNs with IPsec, organizations can establish secure connections for remote access, site-to-site communication, and data privacy.