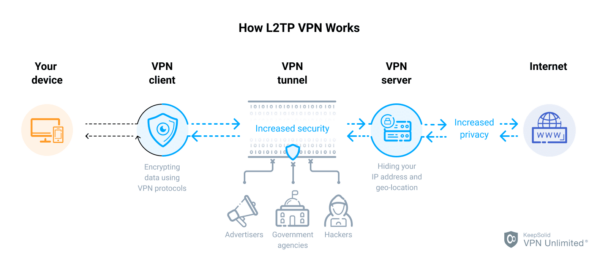
L2TP, or Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol, is a widely-used protocol for creating virtual private networks (VPNs) over the internet or other networks. It operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model and is often used in conjunction with IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) for encryption and authentication, creating a secure tunnel for transmitting data between networks.
Detailed Information about L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol was developed by Cisco and Microsoft in the late 1990s as an extension of two earlier tunneling protocols: Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) and Microsoft’s Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). L2TP combines the best features of both protocols, offering a reliable, secure, and widely interoperable solution for VPN connectivity.
Unlike PPTP, which only supports PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) for data encapsulation, L2TP can encapsulate various network protocols within its tunnels, making it more versatile. Additionally, L2TP does not have the security vulnerabilities associated with PPTP, making it a preferred choice for VPN implementations where security is a concern.
Detailed Analysis of the Key Features of L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
Some key features of L2TP include:
- Encapsulation: L2TP encapsulates data packets with a Layer 2 header, allowing them to traverse networks that use different Layer 2 protocols.
- Compatibility: L2TP is widely supported by networking devices and operating systems, making it easy to implement in diverse environments.
- Security: When used in conjunction with IPsec, L2TP provides strong encryption and authentication mechanisms to secure data transmitted over the VPN tunnel.
- Reliability: L2TP tunnels are highly reliable, with built-in mechanisms for error detection and correction.
- Scalability: L2TP can support a large number of simultaneous VPN connections, making it suitable for enterprise-level deployments.
Types of L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
There are two main types of L2TP:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| L2TPv2 | The original version of L2TP, defined in RFC 2661. It provides basic tunneling capabilities. |
| L2TPv3 | An enhanced version of L2TP, defined in RFC 3931, which supports additional features and options. |
Ways to Use L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
L2TP can be used in various scenarios, including:
- Remote Access VPNs: Providing secure remote access to corporate networks for telecommuters and traveling employees.
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Connecting geographically dispersed offices and branches to form a unified network infrastructure.
- Mobile VPNs: Enabling secure connectivity for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, over public Wi-Fi networks.
Problems and Solutions with L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
Some common issues encountered with L2TP implementations include:
- NAT Traversal: L2TP tunnels may encounter difficulties traversing NAT (Network Address Translation) devices, leading to connectivity issues. This can be addressed by enabling NAT traversal techniques such as UDP encapsulation (L2TP over UDP).
- IPsec Configuration: Configuring IPsec parameters for L2TP/IPsec VPNs can be complex and error-prone. Using automated configuration tools or pre-configured templates can streamline the process and minimize errors.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons with Similar Terms
| Characteristic | L2TP | PPTP | IPsec |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | Requires IPsec for encryption | Vulnerable to security exploits | Provides strong encryption |
| Versatility | Supports various Layer 2 protocols | Limited to PPP encapsulation | Can be used with multiple tunneling protocols |
| Interoperability | Widely interoperable | Limited interoperability | Compatible with most networking devices |
| Overhead | Moderate overhead | Low overhead | Higher overhead due to encryption |
Perspectives and Future Technologies Related to L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
As network technologies continue to evolve, L2TP is likely to remain a relevant and widely-used protocol for VPN connectivity. However, advancements in encryption algorithms, network virtualization, and software-defined networking (SDN) may lead to enhancements and optimizations in L2TP implementations.
VPN Usage Associated with L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
L2TP is commonly used in VPN services, both in commercial offerings and open-source solutions. VPN providers often offer L2TP/IPsec as one of the available VPN protocols due to its compatibility with a wide range of devices and operating systems.
Links to Resources for More Information about L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
For further information about L2TP and its implementations, you can refer to the following resources: