Network security refers to the practice of protecting a computer network infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of service. It involves the implementation of various technologies, policies, and procedures to ensure the security and integrity of data transmitted over a network.
Overview of Network Security
Network security encompasses a broad range of measures aimed at safeguarding networks and the data they transmit. It involves the protection of both hardware and software components, as well as the implementation of protocols and best practices to mitigate potential security threats. Key aspects of network security include:
- Access Control: Limiting access to network resources based on user credentials, roles, or other authentication factors.
- Firewalls: Implementing firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploying systems to detect and respond to unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activity.
- Encryption: Encrypting data to ensure confidentiality and prevent unauthorized interception or eavesdropping.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Establishing secure connections over public networks to enable remote access and protect data in transit.
- Security Auditing and Monitoring: Regularly monitoring network activity and conducting audits to identify potential vulnerabilities or security breaches.
- Patch Management: Keeping systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates to address known vulnerabilities.
Key Features of Network Security
Effective network security solutions typically include the following key features:
- Multi-layered Defense: Combining multiple security measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems, to create a layered defense strategy.
- Real-time Threat Intelligence: Utilizing threat intelligence feeds and automated tools to identify and respond to emerging threats in real-time.
- Scalability: Ensuring that security measures can scale to accommodate the evolving needs and growth of a network infrastructure.
- User Authentication: Implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication, to verify the identity of users accessing the network.
- Centralized Management: Centralizing the management of security policies and configurations to streamline administration and enforcement across the network.
- Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards to protect sensitive data and maintain trust with stakeholders.
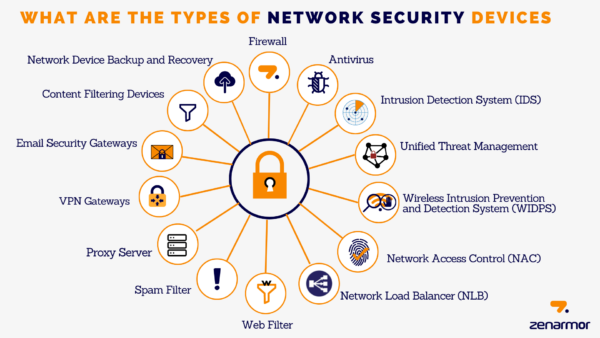
Types of Network Security
Network security encompasses various types of security measures, including:
| Type of Network Security | Description |
|---|---|
| Firewalls | Hardware or software-based barriers that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Systems that detect and alert administrators to potential security threats or breaches. |
| Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) | Systems that actively block or mitigate identified security threats to prevent unauthorized access or damage. |
| Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) | Secure communication tunnels that enable remote users to access a private network securely over a public network, such as the internet. |
| Encryption | The process of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access or interception. |
| Access Control | Mechanisms that restrict access to network resources based on user credentials, roles, or other authentication factors. |
Ways to Use Network Security
Network security can be used in various ways to protect against different types of threats and vulnerabilities, including:
- Securing Data Transmission: Encrypting data to protect it from interception or tampering while in transit over a network.
- Protecting Network Perimeters: Deploying firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor and control traffic entering and exiting a network.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Implementing access control measures to restrict access to sensitive network resources and data.
- Detecting and Responding to Threats: Using intrusion detection and prevention systems to detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Implementing network security measures to comply with relevant regulations and industry standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Challenges and Solutions in Network Security
Despite the benefits of network security, several challenges may arise, including:
- Complexity: Managing and maintaining a comprehensive network security infrastructure can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: The rapid evolution of cyber threats requires constant vigilance and adaptation of security measures.
- User Awareness: Human error remains a significant factor in security breaches, highlighting the importance of ongoing user education and training.
To address these challenges, organizations can adopt the following strategies:
- Automation: Implementing automated tools and processes to streamline security management and response efforts.
- Education and Training: Providing ongoing education and training to employees to raise awareness of security best practices and mitigate the risk of human error.
- Collaboration: Engaging in information sharing and collaboration with industry peers and security experts to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Characteristics and Comparisons
| Characteristic | Network Security | Information Security |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focuses on protecting network infrastructure and data transmission over networks. | Encompasses broader aspects of securing data, including storage, processing, and access control. |
| Implementation | Involves the deployment of hardware and software-based security measures to safeguard network resources. | Involves the implementation of policies, procedures, and technologies to protect sensitive information across various platforms and environments. |
| Key Components | Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption protocols, access control mechanisms, VPNs. | Data encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, security policies and procedures. |
Future Perspectives and Technologies
The future of network security is likely to be shaped by emerging technologies and trends, including:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML-based solutions are increasingly being used to detect and respond to security threats in real-time by analyzing vast amounts of network data.
- Zero Trust Security: The zero-trust model, which assumes that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default, is gaining traction as a more proactive approach to network security.
- Quantum Cryptography: Quantum cryptography holds the promise of secure communication channels immune to eavesdropping or decryption by quantum computers, offering enhanced security for sensitive data transmission.
VPN and Network Security
VPN technology plays a crucial role in enhancing network security by:
- Encrypting Data: VPNs encrypt data transmitted over the internet, protecting it from interception or eavesdropping by unauthorized parties.
- Securing Remote Access: VPNs enable secure remote access to private networks, allowing employees to connect to company resources from any location while maintaining data confidentiality.
- Bypassing Geographical Restrictions: VPNs can be used to bypass geographical restrictions and censorship, enhancing online privacy and freedom of information access.
Resources for Further Information
For more information about network security, consider the following resources:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework
- Cisco Networking Academy
- SANS Institute
By implementing robust network security measures and staying informed about emerging threats and technologies, organizations can effectively protect their networks and data from security breaches and cyber attacks.