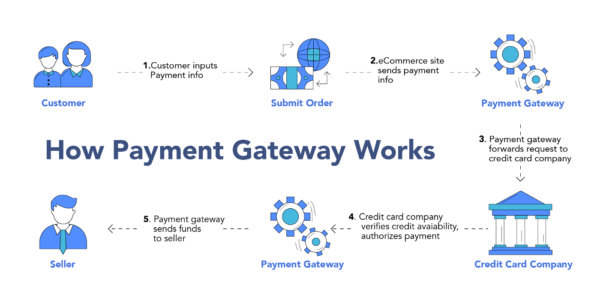
Payment Gateways play a crucial role in the digital transaction landscape, facilitating the secure transfer of payment information from a merchant’s website to the acquiring bank and payment processors. This article delves into the intricacies of Payment Gateways, offering a thorough exploration of their functions, features, types, uses, challenges, and future prospects.
Introduction to Payment Gateways
Payment Gateways are digital platforms that enable online payments for e-commerce sites, online retailers, and any business that accepts payments over the internet. They encrypt sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, to ensure that data passes securely between the customer and the merchant and then between the merchant and the payment processor.
The Mechanics of Payment Gateways
Expanding on the basic definition, Payment Gateways serve as the middleman between a merchant and their bank, facilitating the approval or decline of transactions. They work by encrypting the data provided by the customer, then transmitting it securely to the payment processor used by the merchant’s bank. The payment processor then communicates with the customer’s bank to confirm sufficient funds and account authenticity before approving the transaction.
Key Features of Payment Gateways
- Encryption: Ensures that customer payment information is securely transmitted.
- Authorization: Provides real-time transaction approvals or rejections.
- Fraud Detection: Incorporates tools and algorithms to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions.
- Integration: Offers easy integration with e-commerce platforms and websites.
- Payment Methods: Supports a wide range of payment methods, including credit/debit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets.
Types of Payment Gateways
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Gateways | Process payments directly on the merchant’s website, offering a seamless checkout experience. |
| Redirect Gateways | Redirect customers to the payment gateway’s platform to complete the transaction, then back to the merchant’s site. |
| Hosted Gateways | Collect payment information directly but are hosted off-site, providing a balance between control and security. |
Applications of Payment Gateways
- E-commerce Websites: For processing online sales transactions securely.
- Subscription Services: To manage recurring payments efficiently.
- Mobile Applications: Enabling in-app purchases and transactions.
- B2B Transactions: Facilitating payments between businesses over digital platforms.
Challenges and Solutions in Payment Gateway Usage
Challenges:
- Fraud and Security Risks: High risk of data breaches and fraudulent transactions.
- Integration Issues: Compatibility problems with existing systems and platforms.
- Transaction Fees: Costs associated with processing payments can be high.
Solutions:
- Enhanced Security Measures: Implementing advanced encryption and security protocols.
- Flexible Integration Options: Offering APIs and plugins for various e-commerce platforms.
- Transparent Pricing Models: Clear fee structures with no hidden charges.
Comparative Analysis with Similar Systems
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Merchant Account | Payment Processor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Facilitates the transaction process | Holds funds before transfer | Moves funds from the bank to the merchant |
| Integration | Requires integration with websites | Not directly integrated | Often comes bundled with gateways |
| User Interaction | Direct interaction during payment | No direct user interaction | No direct user interaction |
| Fees | Transaction fees | Account fees, transaction fees | Transaction fees, possibly monthly fees |
Future Trends in Payment Gateway Technology
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: Integration of blockchain technology for secure and decentralized transactions.
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhanced fraud detection and personalized customer experiences.
- Mobile Payment Innovation: Expansion of NFC and mobile wallet capabilities.
- Global Payment Support: Improved support for cross-border transactions and multiple currencies.
The Role of VPN in Enhancing Payment Gateway Security
Utilizing a VPN (Virtual Private Network) can significantly enhance the security of transactions processed through Payment Gateways. VPNs encrypt internet traffic, protecting the data exchange between a customer and the payment gateway from potential intercepts and cyber threats. This additional layer of security is particularly beneficial for mobile transactions and users accessing payment gateways from public or unsecured networks.
Further Reading and Resources
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Guidelines for secure payment processing.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Resources on cybersecurity and encryption standards.
- International Cybersecurity Standards: Information on global cybersecurity practices and protocols.
This comprehensive guide to Payment Gateways underscores their vital role in the modern digital economy, highlighting their features, types, applications, and the challenges they face. As technology evolves, Payment Gateways will continue to adapt, offering more secure, efficient, and user-friendly methods for conducting online transactions.