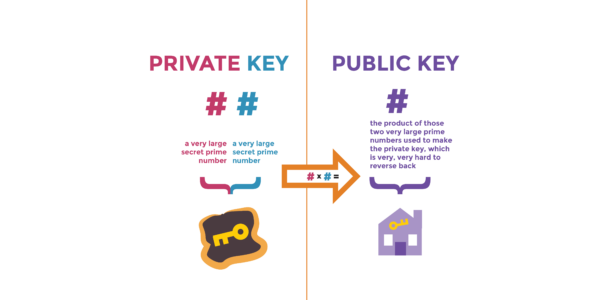
Brief Information about Private Key
A Private Key is a fundamental element in modern cryptography, serving as a crucial component in various cryptographic protocols. It is a sensitive piece of data that is kept secret and used in conjunction with a corresponding Public Key to encrypt and decrypt messages securely.
Detailed Information about Private Key
Private Keys are typically generated by cryptographic algorithms and are unique to each user or entity. They are mathematically linked to their corresponding Public Keys, forming a key pair. While the Public Key is shared openly, the Private Key must be kept confidential to maintain security. Private Keys are used in asymmetric encryption schemes, where data encrypted with a Public Key can only be decrypted with its corresponding Private Key, and vice versa.
Detailed Analysis of the Key Features of Private Key
- Confidentiality: Private Keys must be kept secret to prevent unauthorized access to encrypted data.
- Authentication: Private Keys are used to digitally sign messages, providing a means of verifying the sender’s identity.
- Integrity: By signing messages with Private Keys, the integrity of the data can be ensured, as any tampering would invalidate the signature.
- Non-repudiation: Once a message is signed with a Private Key, the sender cannot deny sending it, adding accountability to communication.
Types of Private Key
Private Keys can be categorized based on the cryptographic algorithms used to generate them:
- RSA Private Key: Generated using the RSA algorithm, commonly used in SSL/TLS certificates.
- DSA Private Key: Utilized in Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) for digital signatures.
- ECDSA Private Key: Derived from the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), offering shorter key lengths with equivalent security.
| Type | Algorithm | Key Length |
|---|---|---|
| RSA Private Key | RSA | Variable |
| DSA Private Key | DSA | 1024, 2048, 3072 bits |
| ECDSA Private Key | ECDSA | 256, 384, 521 bits |
Ways to Use Private Key
- Encryption: Private Keys are used to decrypt data encrypted with their corresponding Public Keys, ensuring confidentiality.
- Digital Signatures: Private Keys sign messages or files to provide authentication and integrity verification.
- Secure Communication: Private Keys facilitate secure communication channels, ensuring that only authorized parties can access transmitted data.
Problems and Solutions with Private Key Usage
- Key Management: Safeguarding Private Keys from theft or loss requires robust key management practices, including secure storage and regular rotation.
- Key Distribution: Ensuring the secure distribution of Public Keys while keeping Private Keys confidential can be challenging. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) addresses this by providing a framework for key management and distribution.
- Key Compromise: If a Private Key is compromised, it can lead to unauthorized access or impersonation. Regularly updating keys and using strong encryption algorithms mitigate this risk.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons with Similar Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Private Key | A cryptographic key kept secret and used for decryption and digital signing. |
| Public Key | A cryptographic key shared openly and used for encryption and verification. |
| Symmetric Key | A single shared key used for both encryption and decryption in symmetric encryption algorithms. |
| Asymmetric Key | A pair of keys (Public and Private) used for encryption and decryption in asymmetric encryption algorithms. |
Perspectives and Future Technologies Related to Private Key
- Quantum Computing: The advent of quantum computers poses a potential threat to traditional cryptographic algorithms used in generating Private Keys. Research into post-quantum cryptography aims to develop algorithms resistant to quantum attacks.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Advances in homomorphic encryption allow computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption, offering new possibilities for secure data processing while maintaining privacy.
VPN and Private Key
VPN (Virtual Private Network) services often utilize encryption protocols that rely on asymmetric cryptography, wherein Private Keys play a crucial role. VPNs use Public and Private Key pairs to establish secure connections between clients and servers, ensuring confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over the network.
Links to Resources
For more information about Private Keys and cryptography:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-57-part-1/rev-5/final
- OpenSSL Documentation – https://www.openssl.org/docs/man1.1.1/
- RSA Security – https://www.rsa.com/en-us/what-is-a-private-key
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of Private Keys, their importance in cryptography, various types, usage scenarios, challenges, and future perspectives. Understanding the significance of Private Keys is essential for ensuring secure communication and protecting sensitive information in today’s digital world.