Brief Information about Risk Management:
Risk management is a crucial process employed by organizations and individuals to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that could impact their objectives. It involves systematic planning, implementation, and monitoring of strategies to minimize the adverse effects of uncertain events. By proactively addressing risks, entities can enhance decision-making, protect assets, and improve overall resilience.
Detailed Information about Risk Management:
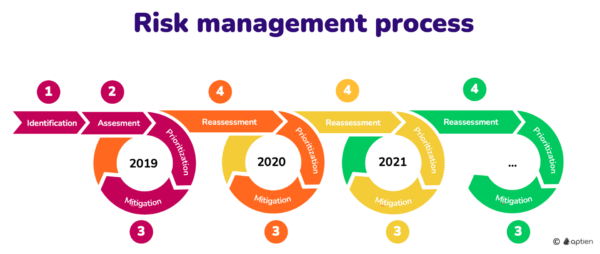
Risk management encompasses several interconnected phases:
- Risk Identification: Recognizing potential risks across various aspects of operations, including financial, operational, strategic, and compliance-related areas.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks to prioritize them based on their severity.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing and implementing strategies to reduce the probability of occurrence or minimize the impact of risks.
- Risk Monitoring and Control: Continuously monitoring the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures and adapting strategies as needed to address emerging threats.
Detailed Analysis of Key Features of Risk Management:
Key features of risk management include:
- Proactivity: Risk management focuses on proactive rather than reactive approaches, enabling organizations to anticipate and address potential threats before they escalate.
- Integration: It should be integrated into overall business processes and decision-making frameworks to ensure alignment with organizational objectives.
- Continual Improvement: Risk management is an iterative process that requires ongoing evaluation and refinement of strategies to adapt to evolving threats and changing business environments.
Types of Risk Management:
Risk management practices can be categorized into several types, including:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Risk Management | Focuses on managing risks related to financial assets, liabilities, and market volatility. |
| Operational Risk Management | Addresses risks arising from internal processes, systems, human error, and external factors. |
| Strategic Risk Management | Involves identifying and mitigating risks associated with long-term strategic objectives and decisions. |
| Compliance Risk Management | Ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards to avoid legal and reputational repercussions. |
Ways to Use Risk Management:
Organizations can leverage risk management in various ways:
- Business Continuity Planning: Implementing risk management strategies to ensure continuity of operations during crises or disruptions.
- Project Management: Integrating risk management into project planning and execution to anticipate and address potential obstacles.
- Investment Decision Making: Utilizing risk management techniques to assess and manage investment risks and optimize returns.
- Insurance Planning: Employing risk management to determine appropriate insurance coverage and minimize financial losses from insurable risks.
Problems Arising with Risk Management and Solutions:
Common challenges in risk management include:
- Lack of Resources: Insufficient budget, expertise, or technology can hinder effective risk management. Solution: Allocate adequate resources and invest in training and technology infrastructure.
- Silos and Fragmentation: Disconnected risk management processes across departments or business units can lead to gaps and inconsistencies. Solution: Foster collaboration and communication among stakeholders and implement integrated risk management systems.
- Overreliance on Models: Relying solely on quantitative models for risk assessment may overlook qualitative factors and lead to inaccurate conclusions. Solution: Balance quantitative analysis with qualitative insights and expert judgment.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons:
| Characteristic | Risk Management | Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Proactively identify and mitigate risks | Transfer financial risk to insurer |
| Scope | Comprehensive approach covering all risks | Focus primarily on insurable risks |
| Strategy | Mitigate, avoid, transfer, or accept risks | Transfer risks to insurer in exchange for premium |
| Outcome | Enhance decision-making and resilience | Financial protection against specified risks |
Perspectives and Technologies of the Future:
Future trends in risk management include:
- Data Analytics: Leveraging advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to analyze large datasets and identify emerging risks.
- Predictive Modeling: Using predictive modeling techniques to forecast potential risks and develop proactive risk management strategies.
- Cyber Risk Management: Addressing the growing threat of cyberattacks through enhanced cybersecurity measures and risk mitigation strategies.
VPN and Risk Management:
VPN (Virtual Private Network) technology can be instrumental in risk management by:
- Enhancing Security: Encrypting data transmissions and providing secure access to network resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Protecting Privacy: Safeguarding sensitive information from interception or surveillance, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with privacy regulations.
- Enabling Remote Work: Facilitating secure remote access to corporate networks and resources, supporting business continuity and risk mitigation efforts during disruptions.
Links to Resources:
For more information about risk management, refer to the following resources: