Brief Information about Security Audit
A Security Audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s information system’s security posture. It involves assessing security policies, procedures, and controls to ensure they are effective in protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access.
Detailed Information about Security Audit
Security Audits play a crucial role in identifying vulnerabilities, assessing risks, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. They typically involve thorough reviews of security policies, configuration settings, access controls, and incident response procedures. By conducting regular audits, organizations can proactively identify and address security weaknesses before they are exploited by malicious actors.
Detailed Analysis of Key Features of Security Audit
Key features of a Security Audit include:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential security risks and vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Checking: Ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Using automated tools to identify weaknesses in the network infrastructure.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating cyber attacks to assess the effectiveness of security controls.
- Incident Response Evaluation: Reviewing procedures for detecting, responding to, and mitigating security incidents.
Types of Security Audit
Security Audits can be categorized into various types based on their scope and objectives:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Internal Audit | Conducted by an organization’s internal team to assess compliance with internal policies and procedures. |
| External Audit | Performed by independent third-party auditors to assess compliance with external regulations and standards. |
| Network Security Audit | Focuses on evaluating the security of the network infrastructure, including firewalls, routers, and intrusion detection systems. |
| Application Security Audit | Examines the security of software applications to identify vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. |
| Compliance Audit | Ensures compliance with specific regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. |
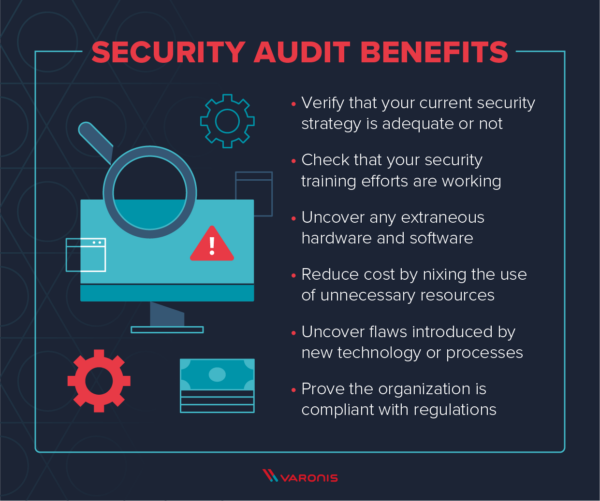
Ways to Use Security Audit
Security Audits serve several purposes, including:
- Identifying security vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Assessing compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of security controls and policies.
- Enhancing the overall security posture of an organization.
- Providing assurance to stakeholders and customers regarding the security of their data.
Problems and Solutions with Security Audit
Common challenges associated with Security Audits include:
- Resource Constraints: Limited budget and manpower for conducting thorough audits.
- Complexity: Managing and interpreting the vast amount of data collected during audits.
- Resistance to Change: Reluctance from stakeholders to implement recommended security measures.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Keeping up with emerging cyber threats and attack techniques.
These challenges can be addressed through:
- Automation: Implementing automated tools for continuous monitoring and auditing.
- Training and Awareness: Educating employees about security best practices and the importance of compliance.
- Collaboration: Working closely with external auditors and security experts to leverage their expertise.
- Regular Updates: Keeping security policies, procedures, and controls up to date to address new threats and vulnerabilities.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons
| Aspect | Security Audit | Penetration Testing | Vulnerability Scanning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | Evaluate security controls and policies. | Simulate cyber attacks to identify weaknesses. | Identify vulnerabilities in network infrastructure. |
| Methodology | Review of policies, procedures, and controls. | Active exploitation of vulnerabilities. | Automated scanning of systems for weaknesses. |
| Frequency | Periodic assessments. | Occasional or continuous. | Continuous monitoring. |
| Scope | Comprehensive assessment of security posture. | Targeted attacks on specific systems or applications. | Broad assessment of network infrastructure. |
Perspectives and Future Technologies
The future of Security Audits is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation. These technologies will enable organizations to conduct more efficient and effective audits by analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and predicting potential security risks. Additionally, blockchain technology holds promise for enhancing the integrity and transparency of audit trails, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of audit findings.
VPN and Security Audit
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) play a crucial role in enhancing the security and privacy of data transmitted over the internet, making them an integral part of Security Audits. By encrypting network traffic and providing secure remote access to corporate resources, VPNs help organizations protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and interception. Additionally, VPNs can be used to anonymize internet traffic, making it more challenging for attackers to track and exploit vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure.
Links to Resources
For more information about Security Audits, you may find the following resources helpful: