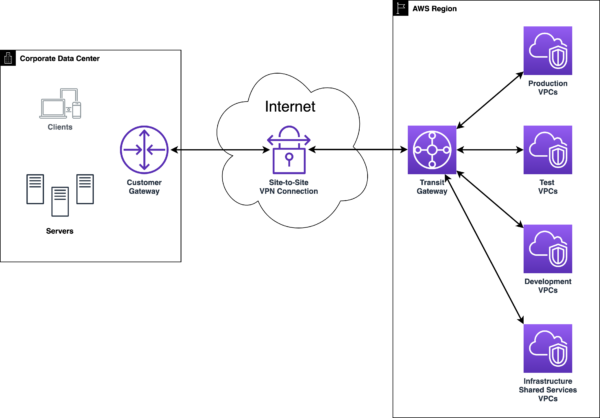
Site-to-Site VPN is a robust networking solution that enables secure and encrypted connections between two or more geographically dispersed sites across the internet. It allows different branches of an organization to share resources as if they were on the same local network, enhancing communication and data sharing across various locations.
Exploring the Fundamentals of Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN constructs a virtual bridge that securely connects networks at different locations over the internet. This technology uses tunneling protocols along with encryption standards to ensure that data transmitted between sites remains private and protected from unauthorized access. By deploying Site-to-Site VPN, organizations can extend their network’s reach, facilitating seamless connectivity between offices, regardless of their physical distance.
Key Features of Site-to-Site VPN
- Encryption and Security: Utilizes advanced encryption standards (AES, DES) to secure data transmissions.
- Authentication: Supports rigorous authentication methods to ensure connections are established between trusted entities.
- Scalability: Easily expands to accommodate growing network requirements without significant infrastructure changes.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduces the need for expensive leased lines, offering a cost-efficient alternative for connecting remote sites.
- Reliability: Provides consistent and stable connectivity, with protocols in place to reroute traffic in case of link failure.
Types of Site-to-Site VPN
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Intranet-based VPN | Connects a company’s multiple sites into a single private network, ideal for internal communication and resource sharing. |
| Extranet-based VPN | Allows a company to connect with external entities (e.g., partners, customers) while maintaining security and privacy. |
| IPsec VPN | Utilizes IPsec protocol for securing internet communication across an IP network, widely used for its robust security features. |
Practical Applications of Site-to-Site VPN
- Remote Workforce Connectivity: Ensures that employees at different locations have secure access to the company’s internal resources.
- Business Expansion: Facilitates seamless integration of new branches or offices into the company’s network.
- Collaboration with Business Partners: Securely shares data with partners or suppliers while maintaining data confidentiality.
Challenges and Solutions in Site-to-Site VPN Deployment
Challenges:
- Complex Configuration: Setting up a Site-to-Site VPN can be technically challenging, requiring specialized knowledge.
- Latency Issues: Can introduce latency, affecting performance, especially for real-time applications.
Solutions:
- Managed VPN Services: Outsourcing to experts can alleviate the burden of complex VPN setup and management.
- Optimization Techniques: Implementing traffic shaping and selecting optimal encryption methods can mitigate latency issues.
Comparative Analysis: Site-to-Site VPN vs. Other VPN Technologies
| Feature | Site-to-Site VPN | Remote Access VPN | Cloud VPN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Connecting multiple sites securely over the internet | Connecting individual users to a network remotely | Connecting users or sites to cloud services |
| Scalability | High, suitable for large organizations | Medium, depends on the number of users | High, designed for cloud scalability |
| Complexity | High, requires careful planning and configuration | Low to medium, user-friendly solutions available | Medium to high, depending on the cloud infrastructure |
Future Trends in Site-to-Site VPN Technology
- Integration with SD-WAN: Enhancing connectivity and security while optimizing network traffic.
- Cloud-Native VPNs: Development of cloud-based VPN solutions for greater flexibility and scalability.
- Advanced Encryption Standards: Adoption of quantum-resistant encryption methods to future-proof security.
Leveraging VPNs in Conjunction with Site-to-Site VPN
Utilizing a Site-to-Site VPN in conjunction with other VPN solutions, such as Remote Access VPNs, can provide comprehensive security coverage. This hybrid approach ensures secure remote access for individual users while maintaining a secure inter-office network.
Further Resources on Site-to-Site VPN
- Cisco Site-to-Site VPN Configuration Guide: A detailed manual on setting up Site-to-Site VPNs using Cisco equipment.
- Microsoft Documentation on VPN Gateway: Offers insights on configuring Site-to-Site VPNs in Azure.
- OpenVPN Access Server User Guide: Provides information on implementing Site-to-Site VPNs with OpenVPN.
This comprehensive guide serves as an encyclopedia on Site-to-Site VPN, offering insights into its fundamentals, applications, challenges, and future directions. Whether for securing communications between office locations or extending network capabilities, Site-to-Site VPN remains a pivotal technology in today’s interconnected world.