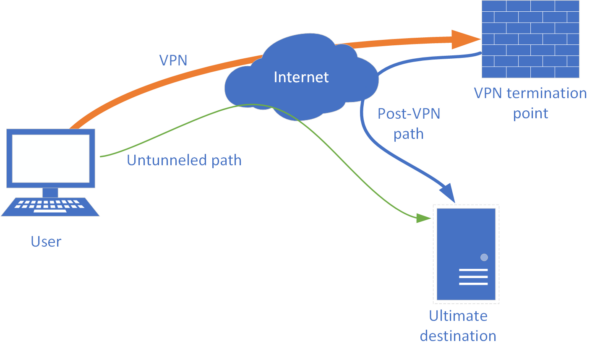
Split tunneling is a networking technique that allows a user to divide their internet traffic into two separate paths: one path travels through the VPN (Virtual Private Network) while the other remains directly connected to the internet without passing through the VPN. This approach contrasts with full tunneling, where all internet traffic is routed through the VPN server. Split tunneling offers users greater control and flexibility over their network traffic, enabling them to optimize performance and security based on their specific needs.
Exploring Split Tunneling
Split tunneling operates by creating two distinct routes for internet traffic: one route directs data through the encrypted VPN tunnel to the VPN server, while the other route sends data directly to the internet without encryption. This division allows users to selectively choose which applications or websites use the VPN connection and which ones access the internet directly. By doing so, users can conserve VPN bandwidth for sensitive or work-related tasks while still accessing local resources or streaming content at optimal speeds.
Analyzing Key Features
Key features of split tunneling include:
- Selective Routing: Users can choose which traffic is routed through the VPN and which traffic bypasses it.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Split tunneling helps optimize bandwidth usage by only routing necessary traffic through the VPN.
- Resource Accessibility: Users can access local network resources, such as printers or file servers, while connected to the VPN.
- Enhanced Performance: By bypassing the VPN for non-sensitive activities, users may experience faster internet speeds for certain tasks.
Types of Split Tunneling
There are two primary types of split tunneling:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Policy-Based | Traffic routing decisions are based on predefined policies set by the network administrator or user. |
| Route-Based | Traffic is routed based on specific network routes or destination IP addresses configured on the device. |
Ways to Use Split Tunneling
Split tunneling can be utilized in various scenarios, including:
- Remote Work: Employees can access corporate resources through the VPN while maintaining direct access to personal applications and services.
- Streaming: Users can stream media content from local or regional services without impacting VPN performance.
- Gaming: Gamers can bypass the VPN for low-latency gaming experiences while keeping sensitive communications secure.
- Web Browsing: Non-sensitive web browsing activities can be conducted directly over the internet for faster speeds.
Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges associated with split tunneling include:
- Security Risks: Direct internet access may expose devices to potential security threats.
- Data Leakage: Improperly configured split tunneling can lead to data leakage if sensitive information travels outside the VPN.
- Policy Enforcement: Ensuring consistent application of split tunneling policies across diverse user devices and network environments can be challenging.
To mitigate these challenges, organizations can implement robust security measures such as:
- Enforcing strict access control policies.
- Implementing endpoint security solutions.
- Regularly auditing and monitoring VPN configurations.
Characteristics and Comparisons
| Characteristic | Split Tunneling | Full Tunneling |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Routing | Selective routing based on user preferences. | All traffic routed through VPN server. |
| Bandwidth Optimization | Optimal usage by routing only necessary traffic. | All traffic consumes VPN bandwidth. |
| Resource Accessibility | Direct access to local network resources. | Limited access to local resources. |
| Performance Impact | Potential performance gains for certain tasks. | Consistent VPN overhead for all activities. |
Future Perspectives
As networks continue to evolve, split tunneling is expected to remain a valuable tool for optimizing network performance and flexibility. Emerging technologies such as Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) may further enhance the capabilities and security of split tunneling deployments.
VPN and Split Tunneling
VPN services often incorporate split tunneling functionality to provide users with greater control over their internet traffic. By integrating split tunneling features into their offerings, VPN providers can cater to diverse user needs, offering both security and performance benefits.
Additional Resources
For more information about split tunneling and its implementation, consider exploring the following resources:
- Understanding Split Tunneling in VPNs
- Best Practices for Split Tunneling Configuration
- Securing Split Tunneling Deployments
Split tunneling offers a versatile solution for balancing security and performance requirements in modern network environments. By understanding its principles and best practices, users and organizations can leverage split tunneling to optimize their network infrastructure effectively.