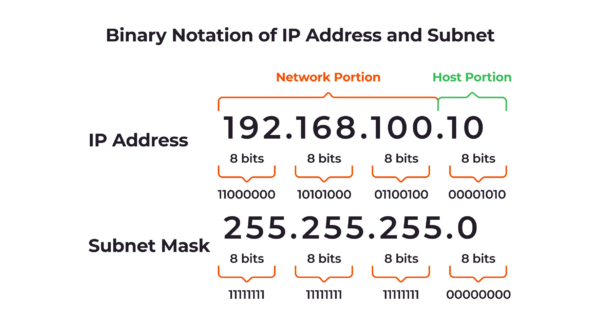
Subnets, short for subnetworks, are a fundamental concept in networking that involves dividing a single large network into smaller, more manageable segments. This division enables efficient data transmission, improved security, and simplified network management.
Exploring Subnet
Subnetting allows network administrators to optimize network performance, enhance security, and efficiently allocate resources. By breaking down a large network into smaller subnets, organizations can better organize their network infrastructure and manage traffic flow effectively.
Key Features of Subnet
Subnetting offers several key features that make it a vital component of modern networking:
- Efficient Address Allocation: Subnetting enables efficient utilization of IP addresses by dividing them into smaller blocks, reducing address wastage.
- Improved Performance: By dividing a large network into smaller subnets, network traffic is localized, leading to reduced congestion and improved overall performance.
- Enhanced Security: Subnetting allows for the implementation of security measures, such as access control lists (ACLs) and firewalls, at the subnet level, increasing network security.
- Simplified Management: Smaller subnets are easier to manage, troubleshoot, and maintain compared to large, monolithic networks.
- Scalability: Subnetting facilitates network growth and scalability by providing a modular approach to network design.
Types of Subnet
Subnets can be categorized based on various criteria, including:
- Classful Subnetting: Based on the traditional IP address classes (A, B, C), where the subnet mask is predefined.
- Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR): Allows for more flexible subnetting by using variable-length subnet masks (VLSM).
- Private Subnets: Reserved IP address ranges for private use within an organization’s internal network.
- Public Subnets: IP address ranges assigned for public-facing network segments, typically connected to the internet.
Uses of Subnet
Subnetting serves various purposes in network design and management:
- Segmentation: Dividing a network into smaller subnets to organize and isolate different departments, functions, or geographical locations.
- Routing Optimization: Subnetting allows for efficient routing of network traffic by directing packets to their intended destinations more directly.
- Resource Allocation: Subnets enable administrators to allocate network resources, such as bandwidth and IP addresses, more effectively based on specific requirements.
- Security Implementation: Subnetting facilitates the implementation of security measures, such as firewall rules and access controls, at a granular level to protect sensitive data and network assets.
Challenges and Solutions
While subnetting offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges:
- Complexity: Subnetting requires careful planning and configuration, which can be challenging for novice network administrators.
- Addressing Scheme Design: Designing an efficient addressing scheme for subnets while avoiding address conflicts and wastage requires expertise.
- Maintenance Overhead: Managing multiple subnets adds complexity to network maintenance tasks, such as addressing changes and troubleshooting.
To address these challenges, organizations can implement robust network management practices, utilize subnet calculators and planning tools, and invest in training for network personnel.
Characteristics and Comparisons
| Characteristic | Subnet | Similar Terms |
|---|---|---|
| Address Allocation | Efficient | Variable |
| Network Segmentation | Granular | Broad |
| Security Implementation | Enhanced | Basic |
| Scalability | Modular | Static |
Future Perspectives
The future of subnetting lies in its continued relevance and adaptation to evolving networking technologies. As networks become increasingly complex and interconnected, subnetting will remain a foundational principle for efficient resource utilization, security enforcement, and scalability.
VPN and Subnet
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can be closely associated with subnetting, especially in enterprise environments where VPNs are used to extend private network connectivity over public networks. VPNs often utilize subnetting to partition network traffic securely and ensure isolation between different VPN clients or networks.
Resources
For more information about subnetting and related networking concepts, refer to the following resources:
- Cisco Networking Academy: Subnetting Basics
- Microsoft Docs: Understanding Subnetting
- Network World: Subnetting Made Easy