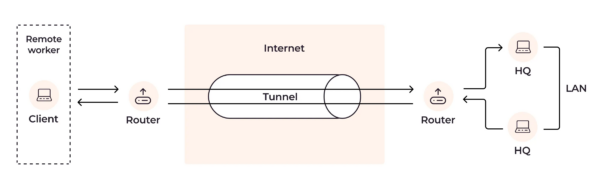
Tunneling is a fundamental technology that enables the secure passage of data between two points over the internet. It forms the backbone of various network protocols, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data as it traverses unsecured networks.
What is Tunneling?
Tunneling encapsulates a network protocol within packets carried by another network protocol. This encapsulation allows for data packets to navigate through a network within another packet, making it possible to use incompatible protocols, bypass firewalls, or maintain privacy and security over public networks.
The Mechanics of Tunneling
Tunneling works by encapsulating a payload protocol, such as HTTP, within a carrier protocol like TCP. The encapsulation process involves adding a header to the payload data, which can then be routed and transferred over the internet or any other network. Upon reaching its destination, the encapsulated data is de-encapsulated, removing the outer header to reveal the original payload, ready for use as intended.
Key Features of Tunneling
Tunneling technologies are characterized by several key features:
- Privacy: Ensures that data is kept confidential during transmission.
- Security: Implements various security measures, including encryption and authentication, to protect data integrity and verify communication parties.
- Bypassing Restrictions: Enables the traversal of network barriers, such as firewalls and NAT (Network Address Translation) systems, facilitating access to restricted networks or services.
- Compatibility: Allows for the communication of different network protocols through encapsulation.
Types of Tunneling
| Type | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Secure Shell (SSH) Tunneling | Uses the SSH protocol to encapsulate data transfers, providing secure channel over an insecure network. | Secure file transfers, remote administration |
| Virtual Private Network (VPN) Tunneling | Establishes a secure and encrypted connection over the internet. | Secure remote access, privacy protection |
| IPsec Tunneling | Provides security for IP communications by enabling encryption and authentication of IP packets. | Secure site-to-site connections |
| SSL/TLS Tunneling | Uses SSL or TLS protocols to secure the connection at the transport layer. | Secure web browsing, secure email transmission |
Applications of Tunneling
Tunneling finds its application in a variety of scenarios, including:
- Secure Communication: Establishing secure and encrypted connections between remote users and networks.
- Bypassing Geo-restrictions: Accessing content or services available only in certain geographical regions.
- Network Management: Facilitating network administration and remote management tasks over secure channels.
- Data Protection: Ensuring the privacy and security of data transmitted over public or untrusted networks.
Challenges and Solutions in Tunneling
Tunneling, while offering numerous benefits, also faces certain challenges:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Latency | Optimization of tunneling protocols and network configurations. |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Regular updates and security patches for tunneling software. |
| Compatibility Issues | Use of standards-based protocols and interoperability testing. |
| Regulatory and Compliance | Adherence to legal and regulatory standards for data protection. |
Comparative Analysis with Similar Technologies
| Feature | Tunneling | Proxy | Direct Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | High (encryption) | Medium (may lack encryption) | Low |
| Privacy | High | Medium | Low |
| Speed | Medium to Low | Medium to High | High |
| Complexity | High | Medium | Low |
| Use Cases | Secure remote access, privacy protection | Bypassing restrictions, anonymity | General internet access |
Future of Tunneling Technologies
The future of tunneling promises advancements in:
- Quantum Encryption: Enhancing security against quantum computing threats.
- AI and ML Optimization: Utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize tunneling protocols and configurations for efficiency and security.
- Integration with IoT: Expanding secure connectivity for the growing network of IoT devices.
Tunneling in the Context of VPNs
VPNs leverage tunneling protocols to create secure and encrypted connections over the internet. This technology is pivotal for VPNs to ensure user data is securely transmitted, maintaining privacy and bypassing internet censorship or geo-restrictions effectively.
Further Reading and Resources
For those seeking to delve deeper into the intricacies of tunneling technologies, the following resources are invaluable:
- IETF RFCs: Technical documents detailing standards and protocols for tunneling technologies.
- Cybersecurity Publications: Articles and white papers on the latest in tunneling security and advancements.
- Networking Tutorials: Online courses and tutorials offering practical insights into tunneling configurations and use cases.
This comprehensive overview underscores the critical role tunneling plays in modern networking, providing the foundation for secure, private, and unrestricted