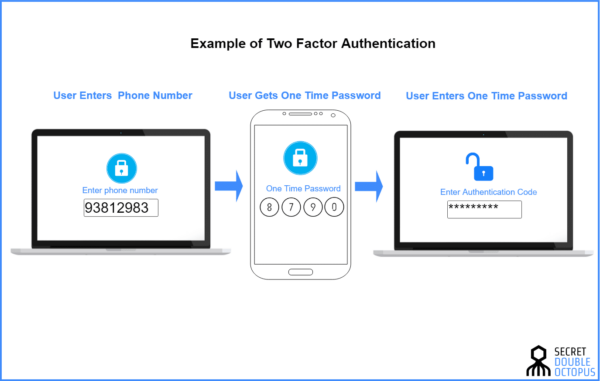
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security mechanism designed to add an extra layer of protection to the standard password-only approach. By requiring two distinct forms of identification before granting access to an account or system, 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, making it a crucial component of modern cybersecurity practices.
The Essence and Importance of Two-Factor Authentication
At its core, two-factor authentication involves the combination of two different types of security credentials. These credentials are categorized into something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (such as a mobile device), or something the user is (including biometrics). This method ensures that even if one factor is compromised, an unauthorized user is unlikely to have access to the second factor, thus maintaining the security of the account or system.
Key Features of Two-Factor Authentication
- Enhanced Security: By requiring a second form of identification, 2FA makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access to sensitive accounts.
- Diverse Methods: 2FA can utilize a range of methods from SMS codes to biometric verification, offering flexibility in how security is implemented.
- User Friendly: Many 2FA systems are designed with ease of use in mind, ensuring that adding extra security does not come at the cost of user convenience.
- Adaptable: With various technologies available, 2FA can be easily integrated into most existing authentication systems.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge-Based | Something the user knows | Passwords, PINs |
| Possession-Based | Something the user has | Security tokens, smartphones |
| Inherence-Based | Something the user is | Fingerprint, facial recognition |
Utilizing Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication can be applied in numerous scenarios, including but not limited to:
- Online Banking: Protecting accounts and transactions.
- Email Services: Securing personal and corporate email accounts.
- Social Media: Enhancing privacy and security on social platforms.
- Cloud Storage: Safeguarding sensitive data stored online.
Challenges and Solutions in Two-Factor Authentication
While 2FA significantly improves security, it is not without its challenges:
- Phishing Vulnerabilities: SMS-based 2FA can be susceptible to phishing attacks. Solution: Use app-based or hardware tokens instead.
- User Inconvenience: Some users may find 2FA methods cumbersome. Solution: Implement user-friendly options like biometrics.
- Technical Issues: Loss of a physical token or device can prevent access. Solution: Offer backup codes and alternative verification methods.
Comparative Overview and Terminology
| Term | Description | Relation to 2FA |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires two or more authentication factors. | 2FA is a type of MFA. |
| Single Sign-On (SSO) | Allows users to log in once and access multiple systems without re-authenticating. | Complementary to 2FA. |
| Biometrics | Use of physical characteristics for identification. | Can be used as a factor in 2FA. |
Future Directions in Two-Factor Authentication
Emerging technologies and perspectives in 2FA include:
- Biometric Advances: Improved accuracy and new forms of biometrics.
- Decentralized Authentication: Blockchain-based methods for more secure and private authentication.
- Adaptive Authentication: Systems that adjust the authentication requirements based on risk assessment.
Enhancing Two-Factor Authentication with VPN
Using a VPN in conjunction with two-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security, particularly in scenarios where network security cannot be guaranteed. A VPN encrypts data transmitted over the internet, protecting the user’s information from interception, which is especially beneficial when using 2FA methods that involve communication over potentially insecure networks.
Further Resources on Two-Factor Authentication
For those interested in exploring two-factor authentication further, the following resources are invaluable:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Offers guidelines and best practices for implementing 2FA.
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA): Provides resources and tools for enhancing cybersecurity, including 2FA.
- Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator: Examples of apps offering 2FA solutions.
In conclusion, two-factor authentication is a critical component of modern cybersecurity, offering enhanced protection for digital assets. By understanding and implementing 2FA, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, safeguarding their information against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.