Brief Overview
An encryption key serves as the cornerstone of data security in the digital realm. It is a string of characters used in conjunction with an encryption algorithm to transform plaintext data into ciphertext and vice versa. Encryption keys play a pivotal role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of sensitive information transmitted over networks or stored on devices.
Detailed Exploration
Encryption keys are essential components of cryptographic systems, serving as the mechanism by which data is secured against unauthorized access or interception. These keys are generated using complex mathematical algorithms and are typically represented as binary or alphanumeric sequences.
Key Features of Encryption Key
- Confidentiality: Encryption keys ensure that only authorized parties can access and decipher encrypted data.
- Integrity: By encrypting data with a key, any unauthorized modifications to the ciphertext can be detected, preserving the integrity of the information.
- Authenticity: Encryption keys help verify the authenticity of encrypted messages, ensuring they originate from legitimate sources.
Types of Encryption Keys
There are several types of encryption keys, each with its own characteristics and applications:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Symmetric Key | Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. Suitable for fast and efficient encryption of large volumes of data. Examples include AES and DES. |
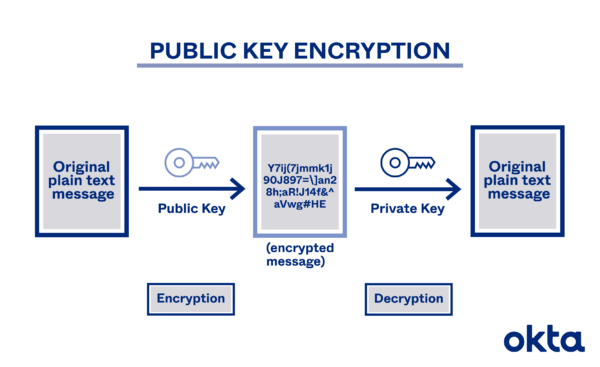
| Asymmetric Key | Involves a pair of keys: one for encryption and another for decryption. Offers enhanced security but is slower than symmetric encryption. Examples include RSA and ECC. |
| Session Key | Temporary keys generated for a specific session or communication exchange. Often used in secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL. |
Uses of Encryption Keys
- Securing communication channels: Encryption keys are utilized to encrypt data transmitted over networks, safeguarding it from eavesdropping and interception.
- Protecting stored data: Encryption keys are employed to encrypt files, databases, and other forms of stored data, preventing unauthorized access in case of theft or unauthorized access to storage devices.
Challenges and Solutions
While encryption keys are integral to data security, several challenges may arise, including:
- Key management: Ensuring secure generation, storage, and distribution of encryption keys.
- Key exchange: Establishing secure channels for exchanging encryption keys between communicating parties.
- Key revocation: Managing the lifecycle of encryption keys and revoking compromised or outdated keys.
These challenges can be addressed through robust key management practices, including the use of hardware security modules (HSMs), key rotation, and multi-factor authentication.
Characteristics and Comparisons
| Characteristic | Encryption Key | Similar Terms |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | High | Variable |
| Key Length | Variable (e.g., 128, 256 bits) | Variable |
| Performance | Depends on algorithm and key size | Varies |
| Security | Crucial for data protection | Essential for privacy |
Future Perspectives
As technology evolves, encryption key technologies are expected to advance, with a focus on:
- Quantum-resistant cryptography: Developing encryption algorithms resilient to attacks from quantum computers.
- Homomorphic encryption: Enabling computation on encrypted data without decrypting it, enhancing privacy in cloud computing and data analytics.
VPN and Encryption Keys
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) leverage encryption keys to establish secure tunnels for transmitting data over public networks. By encrypting network traffic with encryption keys, VPNs ensure confidentiality and privacy for users, shielding their online activities from surveillance or interception.
Resources for Further Information
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – Cryptography: https://csrc.nist.gov/topics/cryptography
- International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR): https://www.iacr.org/
By employing robust encryption key management practices and leveraging encryption technologies, individuals and organizations can enhance the security and privacy of their digital assets in an increasingly interconnected world.